99클럽 | 비기너
🌲 2331. Evaluate Boolean Binary Tree
🏷 Topic : Tree Binary Tree DFS; Depth-First Search
Easy
You are given the root of a full binary tree with the following properties:
- Leaf nodes have either the value
0or1, where0representsFalseand1representsTrue. - Non-leaf nodes have either the value
2or3, where2represents the booleanORand3represents the booleanAND.
The evaluation of a node is as follows:
- If the node is a leaf node, the evaluation is the value of the node, i.e.
TrueorFalse. - Otherwise, evaluate the node's two children and apply the boolean operation of its value with the children's evaluations.
Return the boolean result of evaluating the root node.
A full binary tree is a binary tree where each node has either 0 or 2 children.
A leaf node is a node that has zero children.
Example 1:
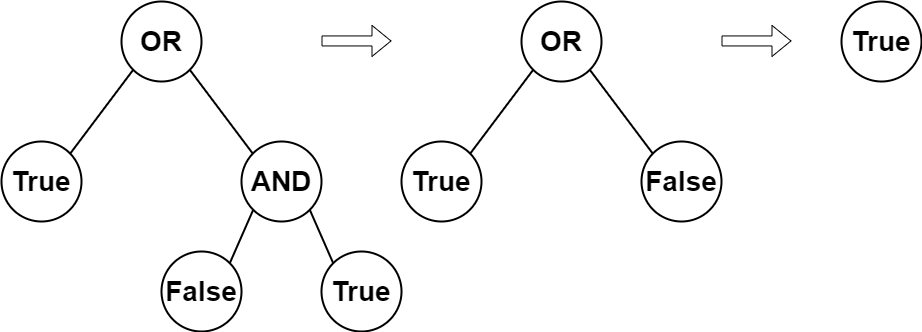
Input: root = [2,1,3,null,null,0,1]
Output: true
Explanation: The above diagram illustrates the evaluation process.
The AND node evaluates to False AND True = False.
The OR node evaluates to True OR False = True.
The root node evaluates to True, so we return true.
Example 2:
Input: root = [0]
Output: false
Explanation: The root node is a leaf node and it evaluates to false, so we return false.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 1000\]. 0 <= Node.val <= 3- Every node has either
0or2children. - Leaf nodes have a value of
0or1. - Non-leaf nodes have a value of
2or3.
Accepted **181.3K** | Submissions **218.5K** | Acceptance Rate **83.0%**
✔ Solution with DFS
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean evaluateTree(TreeNode root) {
boolean result = true;
if (root.left != null) {
if (root.val == 2) {
return evaluateTree(root.left) || evaluateTree(root.right);
} else {
return evaluateTree(root.left) && evaluateTree(root.right);
}
}
if (root.val == 0) {
result = false;
} else if (root.val == 1) {
result = true;
}
return result;
}
}채점 결과
💥 오늘 만난 문제 & 나의 시도 💦 & 해결 방법 👍
오늘 문제도 Tree 문제이다.
오늘도 DFS로 문제를 풀기 위해 재귀함수를 만들어 보았다.
문제를 보면
노드의 값이 0, 1, 2, 3 중 하나인데
리프 노드는 값으로 0 또는 1을 가진다. 이 때, 0은 false, 1은 true를 의미한다.
리프 노드 위의 internal node는 값으로 2 또는 3을 가진다. 이 때, 2는 OR, 3은 AND를 의미한다.
리프 노드의 boolean 값을 그 위의 논리 연산자로 계산해서 root 노드까지 계산한 boolean 값이 얼마가 되는지 구하는 문제이다.
left 리프 노드내부 노드right 리프 노드를 계산한 값을 할당한 boolean 변수 초기화boolean result = true;- 문제에서 Full Binary Tree의 노드를 다루고 있으므로
현재 노드가 리프 노드가 아니면root.left != null이고root.right != null이다.
(참고로 Full Binary Tree는 리프노드가 모두 꽉 차 있다.
그러므로 무조건 left와 right노드가 무조건 존재한다.)- left노드와 right노드의 boolean값을 현재 노드의 값 논리 연산자로 계산한 값을 반환하자.
if (root.left != null) { if (root.val == 2) { return evaluateTree(root.left) || evaluateTree(root.right); } else { return evaluateTree(root.left) && evaluateTree(root.right); } }
- left노드와 right노드의 boolean값을 현재 노드의 값 논리 연산자로 계산한 값을 반환하자.
- 현재 노드가 리프 노드이면
root.val == 0또는root.val == 1이다.- 리프 노드의 값에 대한 boolean 값을
result에 할당.if (root.val == 0) { result = false; } else if (root.val == 1) { result = true; }
- 리프 노드의 값에 대한 boolean 값을
result값을 반환return result;
💬 무엇을 새롭게 알았는지
- Tree와 DFS문제의 다양한 유형을 풀어볼 수 있었다.
📚 References(참고 자료)
[Java 봐 | 자료 구조] 트리(Tree) 개념 정리




