What is Operator?(연산자란?)
- Operation(연산) : 프로그램에서 데이터를 처리하여 결과를 산출하는 것
- Operator(연산자) : 연산에 사용되는 표시나 기호
- Operand(피연산자) : 연산되는 데이터
연산자의 종류
- 증감 연산자 :
++,--(1순위) - 산술 연산자 :
+,-,*,/,%(2순위) - 시프트 연산자 :
>>,<<,>>>(3순위) - 비교 연산자 :
>,<,>=,<=,==,!=(4순위) - 비트 연산자 :
&,|,^,~(~만 1순위, 나머지는 5순위) - 논리 연산자 :
&&,||,!(!만 1순위, 나머지는 6순위) - 조건(삼항) 연산자 :
?,:(7순위) - 대입 연산자 :
=,*=,/=,%=,+=,-=(8순위)
Increment and Decrement Operators(증감 연산자)
피연산자의 값을 1씩 증가 또는 감소시키는 연산자
x++,++x,x--,--x
※ 증감 연산자가 변수 앞에 위치하느냐 변수 뒤에 위치하느냐에 따라 결과 값이 달라진다.
후행(후위) 증가 연산자 (x++)
먼저 해당 연산을 수행한 후 피연산자의 값을 1 증가 시킴.
// 후행(후위) 증가 연산자 int x = 10; int y = x++; // y = x; // x = x + 1; System.out.println("== 후행(후위) 증가 연산자 =="); System.out.println("x = " + x); System.out.println("y = " + y);Output(출력)
== 후행(후위) 증가 연산자 == x = 11 y = 10
선행(전위) 증가 연산자 (++x)
먼저 피연산자의 값을 1 증가 시킨 후 해당 연산을 수행 함.
// 선행(전위) 증가 연산자 int x = 10; int y = ++x; // x = x + 1; // y = x; System.out.println("== 선행(전위) 증가 연산자 =="); System.out.println("x = " + x); System.out.println("y = " + y);Output(출력)
== 선행(전위) 증가 연산자 == x = 11 y = 11
후행(후위) 감소 연산자 (x--)
먼저 해당 연산을 수행한 후 피연산자의 값을 1 감소 시킴.
// 후행(후위) 감소 연산자 int x = 10; int y = x--; // y = x; // x = x - 1; System.out.println("== 후행(후위) 감소 연산자 =="); System.out.println("x = " + x); System.out.println("y = " + y);Output(출력)
== 후행(후위) 감소 연산자 == x = 9 y = 10
선행(전위) 감소 연산자 (--x)
먼저 피연산자의 값을 1 감소 시킨 후 해당 연산을 수행 함.
// 선행(전위) 감소 연산자 int x = 10; int y = --x; // x = x - 1; // y = x; System.out.println("== 선행(전위) 감소 연산자 =="); System.out.println("x = " + x); System.out.println("y = " + y);Output(출력)
== 선행(전위) 감소 연산자 == x = 9 y = 9
🔝 Click here to go to the list of operaters!
(여기를 클릭하여 연산자 리스트로 가세요.)
Arithmetic Operator(산술 연산자)
4칙 연산(
+,-,*,/), 나머지 연산자(%)
덧셈 연산자 (+)
두 수에 대한 덧셈
int x = 10; System.out.println("== 덧셈 연산자 =="); System.out.println("x = " + x); System.out.println("x + 3 = " + (x + 3));Output(출력)
== 덧셈 연산자 == x = 10 x + 3 = 13
뺄셈 연산자 (-)
두 수에 대한 뺄셈
int x = 10; System.out.println("== 뺄셈 연산자 =="); System.out.println("x = " + x); System.out.println("x - 3 = " + (x - 3));Output(출력)
== 뺄셈 연산자 == x = 10 x - 3 = 7
곱셈 연산자 (*)
두 수에 대한 곱셈
int x = 10; System.out.println("== 곱셈 연산자 =="); System.out.println("x = " + x); System.out.println("x * 3 = " + (x * 3));Output(출력)
== 곱셈 연산자 == x = 10 x * 3 = 30
나눗셈 연산자 (/)
두 수에 대한 나눗셈
int x = 10; System.out.println("== 나눗셈 연산자 =="); System.out.println("x = " + x); System.out.println("x / 3 = " + (x / 3)); System.out.println("x / 2 = " + (x / 2));Output(출력)
== 나눗셈 연산자 == x = 10 x / 3 = 3 x / 2 = 5
변수 x의 자료형이 int type이기 때문에 나눗셈 결과값도 int type으로 반환.
∴ x ÷ 3 = 3.333...에서 소숫점 아랫부분을 버림하고 x / 3 = 3
나머지 연산자 (%)
왼쪽 피연산자의 값을 오른쪽 피연산자의 값으로 나눈 나머지 값을 반환
( x % n )의 경우 x의 값에 관계 없이 결과값의 범위가 0 ~ n-1 이 됨.
ex) ( x % 7 ) 연산의 값의 범위는 0 ~ 6결과값이 회귀하게 되어서 알고리즘 구현에 자주 사용되는 연산자
int x = 1234; System.out.println("== 나머지 연산자 =="); System.out.println("x = " + x); System.out.println("x % 7 = " + (x % 7)); // 0 ~ 6 사이의 값을 반환 System.out.println("x % 2 = " + (x % 2)); // 0 또는 1 값을 반환 // x값이 홀수인지 짝수인지 구분에 유용Output(출력)
== 나머지 연산자 == x = 1234 x % 7 = 2 x % 2 = 0
Shift Operator(시프트 연산자)
bit단위의 연산 처리를 함.
자료의 가공을 위해 오른쪽 또는 왼쪽으로 이동하여 값에 대한 변화를 일으키는 연산자<<,>>,>>>
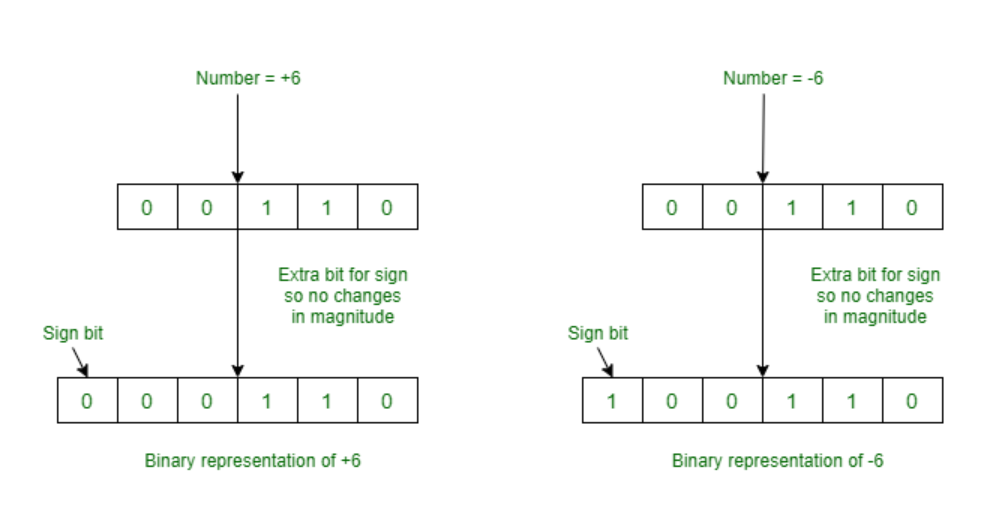
비트의 음수 표현
2진수로 음수를 표현하는 방법(3가지)
최상위 비트(가장 좌측의 비트)를 부호를 표현하는 비트로 사용
최상위 비트가 0이면 양수
최상위 비트가 1이면 음수
- 부호 및 크기 방식
- 1진 보수방식
- 2진 보수방식
1. 부호 및 크기 방식
최상위 비트는 부호를 나머지 비트는 크기를 나타내는 방식
0의 두가지 표현 방식이 나오며 비트 연산의 어려움이 있음.
001001 + 101001 = 110010
<!-- 십진법 계산 -->
9 + (-9) = -18 // 계산이 제대로 되지 않는다.
2. 1진 보수 방법
1의 보수 : 어떤 수를 2ⁿ-1로 만들어 주는 수
이진수에서 모든 비트의 숫자를 반전시키면 얻을 수 있다.
어떤 수와 반전시킨 수를 더하면 모든 비트가 1로 채워진 2ⁿ-1 이 됨.
비트 연산을 가능하게 하는 방법이지만 역시 0의 표현 방식이 두가지가 나온다.


3. 2진 보수 방법
2의 보수 : 어떤 수를 2ⁿ으로 만들어 주는 수로 1의 보수를 취한 후, 1을 더해준다.
0의 표현 방법이 하나(= 0000)
비트 연산도 가능
대부분의 프로그래밍 언어에서 사용하는 방식


Left Shift Operator(왼쪽 쉬프트 연산) (<<)
bit 값을 왼쪽으로 이동(빈 자리는 0으로 대입)
( x << n ) = x * 2ⁿ
Integer.MAX_VALUE's bit exp는 1111111111111111111111111111111 : 총 32자리 숫자
즉, n이 32 이상이면, ( x << n ) = x * 2^(n % 32)

int x = 64;
int n = 2;
System.out.println("== 왼쪽 쉬프트 연산자 ==");
System.out.println("x << n = " + (x << n)); // 곱셈, (x * 2ⁿ)
System.out.println("x << 34 = " + (x << 34)); // x * 2^(n % 32)
System.out.println("x's bit exp: " + Integer.toBinaryString(x));
System.out.println("x << n: " + Integer.toBinaryString(x << n));Output(출력)
== 왼쪽 쉬프트 연산자 ==
x << n = 256
x << 34 = 256
x's bit exp: 1000000
x << n: 100000000Right Shift Operator(오른쪽 쉬프트 연산) (>>)
bit 값을 오른쪽으로 이동
이동에 따른 빈공간은 음수의 경우엔 1, 양수인 경우엔 0으로 채움
( x >> n ) = x / 2ⁿ
n이 32이상이면, ( x >> n ) = x / 2^(n % 32)

int x = 64;
int n = 2;
System.out.println("== 오른쪽 쉬프트 연산자(양수 피연산자) ==");
System.out.println("x >> n = " + (x >> n)); // 나눗셈, (x / 2ⁿ)
System.out.println("x >> 34 = " + (x >> 34)); // x / 2^(n % 32)
System.out.println("x's bit exp: " + Integer.toBinaryString(x));
System.out.println("x >> n: " + Integer.toBinaryString(x >> n));Output(출력)
== 오른쪽 쉬프트 연산자 ==
x >> n = 16
x >> 34 = 16
x's bit exp: 1000000
x >> n: 10000int x = -64;
int n = 2;
System.out.println("== 오른쪽 쉬프트 연산자(음수 피연산자) ==");
System.out.println("x >> n = " + (x >> n)); // 나눗셈, (x / 2ⁿ)
System.out.println("x >> 34 = " + (x >> 34)); // x / 2^(n % 32)
System.out.println("x's bit exp: " + Integer.toBinaryString(x));
System.out.println("x >> n: " + Integer.toBinaryString(x >> n));Output(출력)
== 오른쪽 쉬프트 연산자(음수 피연산자) ==
x >> n = -16
x >> 34 = -16
x's bit exp: 11111111111111111111111111000000
x >> n: 11111111111111111111111111110000Unsigned Shift Operator (>>>)
bit 값을 오른쪽으로 이동(밀어버린 부분을 전부 0으로 챙워줌.)
음수를 보장하지 않습니다.


int x = 64;
int n = 2;
System.out.println("== Unsigned 쉬프트 연산자 ==");
System.out.println("x >>> n = " + (x >>> n));
System.out.println("x >>> 34 = " + (x >>> 34));
System.out.println("x's bit exp: " + Integer.toBinaryString(x));
System.out.println("x >>> n: " + Integer.toBinaryString(x >>> n));Output(출력)
== Unsigned 쉬프트 연산자 ==
x >>> n = 16
x >>> 34 = 16
x's bit exp: 1000000
x >>> n: 10000🔝 Click here to go to the list of operaters!
(여기를 클릭하여 연산자 리스트로 가세요.)
Relational Operator(비교 연산자)
변수나 상수의 값을 비교할 때 쓰이는 연산자
결과가 항상true또는false인 논리값(Boolean)>,<,>=,<=,==,!=
크다 (>)
int x = 12; System.out.println("x = " + x); System.out.println("x > 10 = " + (x > 10)); System.out.println("x > 12 = " + (x > 12)); System.out.println("x > 15 = " + (x > 15));Output(출력)
x = 12 x > 10 = true x > 12 = false x > 15 = false
작다 (<)
int x = 12; System.out.println("x = " + x); System.out.println("x < 10 = " + (x < 10)); System.out.println("x < 12 = " + (x < 12)); System.out.println("x < 15 = " + (x < 15));Output(출력)
x = 12 x < 10 = false x < 12 = false x < 15 = true
크거나 같다 (>=)
int x = 12; System.out.println("x = " + x); System.out.println("x >= 10 = " + (x >= 10)); System.out.println("x >= 12 = " + (x >= 12)); System.out.println("x >= 15 = " + (x >= 15));Output(출력)
x = 12 x >= 10 = true x >= 12 = true x >= 15 = false
작거나 같다 (<=)
int x = 12; System.out.println("x = " + x); System.out.println("x <= 10 = " + (x <= 10)); System.out.println("x <= 12 = " + (x <= 12)); System.out.println("x <= 15 = " + (x <= 15));Output(출력)
x = 12 x <= 10 = false x <= 12 = true x <= 15 = true
같다 (==)
int x = 12; System.out.println("x = " + x); System.out.println("x == 10 = " + (x == 10)); System.out.println("x == 12 = " + (x == 12)); System.out.println("x == 15 = " + (x == 15));Output(출력)
x = 12 x == 10 = false x == 12 = true x == 15 = false
같지 않다 (!=)
int x = 12; System.out.println("x = " + x); System.out.println("x != 10 = " + (x != 10)); System.out.println("x != 12 = " + (x != 12)); System.out.println("x != 15 = " + (x != 15));Output(출력)
x = 12 x != 10 = true x != 12 = false x != 15 = true
🔝 Click here to go to the list of operaters!
(여기를 클릭하여 연산자 리스트로 가세요.)
Bitwise Operator(비트 연산자)
비트(bit) 단위로 논리 연산을 할 때 사용하는 연산자
비트 단위로 왼쪽이나 오른쪽으로 전체 비트를 이동하거나,
1의 보수를 만들 때 사용&,|,^,~, 쉬프트 연산자(>>,<<,>>>)
쉬프트 연산자도 비트 연산자에 포함됨
비트 AND 연산 (&)
대응되는 비트가 모두 1이면 1을 반환
0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 & & & & & & & & 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 int x = 0B00001111; int y = 0B00010101; System.out.printf("%-8s","x = "); System.out.println(String.format("%8s",Integer.toBinaryString(x)).replace(" ", "0")); System.out.printf("%-8s","y = "); System.out.println(String.format("%8s",Integer.toBinaryString(y)).replace(" ", "0")); System.out.printf("%-8s","x & y = "); System.out.println(String.format("%8s",Integer.toBinaryString(x & y)).replace(" ", "0"));Output(출력)
x = 00001111 y = 00010101 x & y = 00000101
비트 OR 연산 (|)
대응되는 비트 중에서 하나라도 1이면 1을 반환
0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 | | | | | | | | 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 int x = 0B00001111; int y = 0B00010101; System.out.printf("%-8s","x = "); System.out.println(String.format("%8s",Integer.toBinaryString(x)).replace(" ", "0")); System.out.printf("%-8s","y = "); System.out.println(String.format("%8s",Integer.toBinaryString(y)).replace(" ", "0")); System.out.printf("%-8s","x | y = "); System.out.println(String.format("%8s",Integer.toBinaryString(x | y)).replace(" ", "0"));Output(출력)
x = 00001111 y = 00010101 x | y = 00011111
비트 XOR 연산 (^)
대응되는 비트가 서로 다르면 1을 반환
0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 int x = 0B00001111; int y = 0B00010101; System.out.printf("%-8s","x = "); System.out.println(String.format("%8s",Integer.toBinaryString(x)).replace(" ", "0")); System.out.printf("%-8s","y = "); System.out.println(String.format("%8s",Integer.toBinaryString(y)).replace(" ", "0")); System.out.printf("%-8s","x ^ y = "); System.out.println(String.format("%8s",Integer.toBinaryString(x ^ y)).replace(" ", "0"));Output(출력)
x = 00001111 y = 00010101 x ^ y = 00011010
비트 NOT 연산 (~)
비트가 1이면 0을 반환
비트가 0이면 1을 반환 (1의 보수)~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 int x = 0B00001111; String not_x = Integer.toBinaryString(~x); not_x = not_x.substring(not_x.length()-8, not_x.length()); System.out.printf("%5s %s\n", "x = ", String.format("%8s",Integer.toBinaryString(x)).replace(" ","0")); System.out.printf("%5s %s\n", "~x = ", not_x); int y = 0B00010101; String not_y = Integer.toBinaryString(~y); not_y = not_y.substring(not_y.length()-8, not_y.length()); System.out.printf("%5s %s\n", "y = ", String.format("%8s",Integer.toBinaryString(y)).replace(" ","0")); System.out.printf("%5s %s\n", "~y = ", not_y);Output(출력)
x = 00001111 ~x = 11110000 y = 00010101 ~y = 11101010
비트 연산자의 진리표(truth table)
| X | Y | X|Y | X&Y | X^Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
🔝 Click here to go to the list of operaters!
(여기를 클릭하여 연산자 리스트로 가세요.)
Logical Operator(논리 연산자)
주어진 논리식을 판단하여
true(참)과false(거짓)을 결정하는 연산자&&,||,!
논리 연산자의 종류(1)
- 논리 AND 연산(논리곱; &&)
논리식이 모두 참이면 참을 반환
boolean result1 = true, result2 = true;
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
System.out.println("results1 && result2 = " + (result1 && result2) + "\n");
result1 = true;
result2 = false;
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
System.out.println("results1 && result2 = " + (result1 && result2) + "\n");
result1 = false;
result2 = true;
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
System.out.println("results1 && result2 = " + (result1 && result2) + "\n");
result1 = false;
result2 = false;
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
System.out.println("results1 && result2 = " + (result1 && result2));Output(출력)
result1 = true
result2 = true
results1 && result2 = true
result1 = true
result2 = false
results1 && result2 = false
result1 = false
result2 = true
results1 && result2 = false
result1 = false
result2 = false
results1 && result2 = false- 논리 OR 연산(논리합; ||)
논리식 중 하나라도 참이면 참을 반환
boolean result1 = true, result2 = true;
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
System.out.println("results1 || result2 = " + (result1 || result2) + "\n");
result1 = true;
result2 = false;
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
System.out.println("results1 || result2 = " + (result1 || result2) + "\n");
result1 = false;
result2 = true;
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
System.out.println("results1 || result2 = " + (result1 || result2) + "\n");
result1 = false;
result2 = false;
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
System.out.println("results1 || result2 = " + (result1 || result2));Output(출력)
result1 = true
result2 = true
results1 || result2 = true
result1 = true
result2 = false
results1 || result2 = true
result1 = false
result2 = true
results1 || result2 = true
result1 = false
result2 = false
results1 || result2 = false- 논리 NOT 연산(부정; !)
논리식의 결과가 참이면 거짓을 반환
논리식의 결과가 거짓이면 참을 반환
boolean result1 = true, result2 = true;
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
System.out.println("results1 != result2 = " + (result1 != result2) + "\n");
result1 = true;
result2 = false;
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
System.out.println("results1 != result2 = " + (result1 != result2) + "\n");
result1 = false;
result2 = true;
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
System.out.println("results1 != result2 = " + (result1 != result2) + "\n");
result1 = false;
result2 = false;
System.out.println("result1 = " + result1);
System.out.println("result2 = " + result2);
System.out.println("results1 != result2 = " + (result1 != result2));Output(출력)
result1 = true
result2 = true
results1 != result2 = false
result1 = true
result2 = false
results1 != result2 = true
result1 = false
result2 = true
results1 != result2 = true
result1 = false
result2 = false
results1 != result2 = false논리연산자의 종류(2)
논리곱 (&&)
선조건이
true일 때만 후조건을 실행
선조건이false이면 후조건을 실행하지 않는다.boolean result1 = true, result2 = true; System.out.println("result1 = " + result1); System.out.println("result2 = " + result2); System.out.println("results1 && result2 = " + (result1 && result2) + "\n"); result1 = true; result2 = false; System.out.println("result1 = " + result1); System.out.println("result2 = " + result2); System.out.println("results1 && result2 = " + (result1 && result2) + "\n"); result1 = false; result2 = true; System.out.println("result1 = " + result1); System.out.println("result2 = " + result2); System.out.println("results1 && result2 = " + (result1 && result2) + "\n"); result1 = false; result2 = false; System.out.println("result1 = " + result1); System.out.println("result2 = " + result2); System.out.println("results1 && result2 = " + (result1 && result2));Output(출력)
result1 = true result2 = true results1 && result2 = true result1 = true result2 = false results1 && result2 = false result1 = false result2 = true results1 && result2 = false result1 = false result2 = false results1 && result2 = false
||
선조건이
true이면 후조건을 실행하지 않으며
선조건이false일 때만 후조건을 실행한다.boolean result1 = true, result2 = true; System.out.println("result1 = " + result1); System.out.println("result2 = " + result2); System.out.println("results1 || result2 = " + (result1 || result2) + "\n"); result1 = true; result2 = false; System.out.println("result1 = " + result1); System.out.println("result2 = " + result2); System.out.println("results1 || result2 = " + (result1 || result2) + "\n"); result1 = false; result2 = true; System.out.println("result1 = " + result1); System.out.println("result2 = " + result2); System.out.println("results1 || result2 = " + (result1 || result2) + "\n"); result1 = false; result2 = false; System.out.println("result1 = " + result1); System.out.println("result2 = " + result2); System.out.println("results1 || result2 = " + (result1 || result2));Output(출력)
result1 = true result2 = true results1 || result2 = true result1 = true result2 = false results1 || result2 = true result1 = false result2 = true results1 || result2 = true result1 = false result2 = false results1 || result2 = false
논리 연산자의 진리표(truth table)
| A | B | A && B | A || B | !A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| true | true | true | true | false |
| true | false | false | true | false |
| false | true | false | true | true |
| false | false | false | false | true |
🔝 Click here to go to the list of operaters!
(여기를 클릭하여 연산자 리스트로 가세요.)
Assignment Operator(대입 연산자)
변수에 값을 대입할 때 사용하는 이항 연산자
피연산자들의 결합 방향은 오른쪽에서 왼쪽=,+=,-=,*=,/=,%=,&=,|=,^=,<<=,>>=,>>>=
=
왼쪽의 피연산자에 오른쪽의 피연산자를 대입함.
int x = 120; System.out.println("x = " + x); int y = 0; System.out.println("y = " + y); y = x; System.out.println("y = " + y);Output(출력)
x = 120 y = 0 y = 120
+=
왼쪽의 피연산자에 오른쪽의 피연산자를 더한 후, 그 결과값을 왼쪽의 피연산자에 대입함.
int x = 120; System.out.println("x = " + x); x += 1; System.out.println("x += 1 >> x = " + x); int y = 10; System.out.println("y = " + y); x += y; System.out.println("x += y >> y = " + x);Output(출력)
x = 120 x += 1 >> x = 121 y = 10 x += y >> y = 131
-=
왼쪽의 피연산자에서 오른쪽의 피연산자를 뺀 후, 그 결과값을 왼쪽의 피연산자에 대입함.
int x = 120; System.out.println("x = " + x); x -= 1; System.out.println("x -= 1 >> x = " + x); int y = 10; System.out.println("y = " + y); x -= y; System.out.println("x -= y >> y = " + x);Output(출력)
x = 120 x -= 1 >> x = 119 y = 10 x -= y >> y = 109
*=
왼쪽의 피연산자에 오른쪽의 피연산자를 곱한 후, 그 결과값을 왼쪽의 피연산자에 대입함.
int x = 120; System.out.println("x = " + x); x *= 2; System.out.println("x *= 2 >> x = " + x); int y = 10; System.out.println("y = " + y); x *= y; System.out.println("x *= y >> y = " + x);Output(출력)
x = 120 x *= 2 >> x = 240 y = 10 x *= y >> y = 2400
/=
왼쪽의 피연산자를 오른쪽의 피연산자로 나눈 후, 그 결과값을 왼쪽의 피연산자에 대입함.
int x = 120; System.out.println("x = " + x); x /= 2; System.out.println("x /= 2 >> x = " + x); int y = 10; System.out.println("y = " + y); x /= y; System.out.println("x /= y >> y = " + x);Output(출력)
x = 120 x /= 2 >> x = 60 y = 10 x /= y >> y = 6
%=
왼쪽의 피연산자를 오른쪽의 피연산자로 나눈 후, 그 나머지를 왼쪽의 피연산자에 대입함.
int x = 120; System.out.println("x = " + x); x %= 7; System.out.println("x %= 7 >> x = " + x); x = 120; int y = 10; System.out.println("x = " + x + ", y = " + y); x %= y; System.out.println("x %= y >> y = " + x);Output(출력)
x = 120 x %= 7 >> x = 1 x = 120, y = 10 x %= y >> y = 0
&=
왼쪽의 피연산자를 오른쪽의 피연산자와 비트 AND 연산한 후, 그 결과값을 왼쪽의 피연산자에 대입함.
int x = 0B00001111; int y = 0B00010101; System.out.printf("%14s","x = "); System.out.println(String.format("%8s",Integer.toBinaryString(x)).replace(" ", "0")); System.out.printf("%14s","y = "); System.out.println(String.format("%8s",Integer.toBinaryString(y)).replace(" ", "0")); x &= y; System.out.printf("%14s","x &= y >> x = "); System.out.println(String.format("%8s",Integer.toBinaryString(x)).replace(" ", "0"));Output(출력)
x = 00001111 y = 00010101 x &= y >> x = 00000101
|=
왼쪽의 피연산자를 오른쪽의 피연산자와 비트 OR 연산한 후, 그 결과값을 왼쪽의 피연산자에 대입함.
int x = 0B00001111; int y = 0B00010101; System.out.printf("%14s","x = "); System.out.println(String.format("%8s",Integer.toBinaryString(x)).replace(" ", "0")); System.out.printf("%14s","y = "); System.out.println(String.format("%8s",Integer.toBinaryString(y)).replace(" ", "0")); x |= y; System.out.printf("%14s","x |= y >> x = "); System.out.println(String.format("%8s",Integer.toBinaryString(x)).replace(" ", "0"));Output(출력)
x = 00001111 y = 00010101 x |= y >> x = 00011111
^=
왼쪽의 피연산자를 오른쪽의 피연산자와 비트 XOR 연산한 후, 그 결과값을 왼쪽의 피연산자에 대입함.
int x = 0B00001111; int y = 0B00010101; System.out.printf("%14s","x = "); System.out.println(String.format("%8s",Integer.toBinaryString(x)).replace(" ", "0")); System.out.printf("%14s","y = "); System.out.println(String.format("%8s",Integer.toBinaryString(y)).replace(" ", "0")); x ^= y; System.out.printf("%14s","x ^= y >> x = "); System.out.println(String.format("%8s",Integer.toBinaryString(x)).replace(" ", "0"));Output(출력)
x = 00001111 y = 00010101 x ^= y >> x = 00011010
<<=
왼쪽의 피연산자를 오른쪽의 피연산자만큼 왼쪽 시프트한 후, 그 결과값을 왼쪽의 피연산자에 대입함.
int x = 0B00001111; System.out.printf("%15s","x = "); System.out.println(String.format("%32s",Integer.toBinaryString(x)).replace(" ", "0")); x <<= 3; System.out.printf("%-11s","x <<= 3; "); System.out.println("x = " + String.format("%32s",Integer.toBinaryString(x)).replace(" ", "0"));Output(출력)
x = 00000000000000000000000000001111 x <<= 3; x = 00000000000000000000000001111000
int x = -0B00001111; System.out.printf("%15s","x = "); System.out.println(String.format("%32s",Integer.toBinaryString(x)).replace(" ", "0")); x <<= 3; System.out.printf("%-11s","x <<= 3; "); System.out.println("x = " + String.format("%32s",Integer.toBinaryString(x)).replace(" ", "0"));Output(출력)
x = 11111111111111111111111111110001 x <<= 3; x = 11111111111111111111111110001000
>>=
왼쪽의 피연산자를 오른쪽의 피연산자만큼 왼쪽 시프트한 후, 그 결과값을 왼쪽의 피연산자에 대입함.
int x = 0B00001111; System.out.printf("%15s","x = "); System.out.println(String.format("%32s",Integer.toBinaryString(x)).replace(" ", "0")); x >>= 3; System.out.printf("%-11s","x >>= 3; "); System.out.println("x = " + String.format("%32s",Integer.toBinaryString(x)).replace(" ", "0"));Output(출력)
x = 00000000000000000000000000001111 x >>= 3; x = 00000000000000000000000000000001
int x = -0B00001111; System.out.printf("%15s","x = "); System.out.println(String.format("%32s",Integer.toBinaryString(x)).replace(" ", "0")); x >>= 3; System.out.printf("%-11s","x >>= 3; "); System.out.println("x = " + String.format("%32s",Integer.toBinaryString(x)).replace(" ", "0"));Output(출력)
x = 11111111111111111111111111110001 x >>= 3; x = 11111111111111111111111111111110
>>>=
왼쪽의 피연산자를 오른쪽의 피연산자만큼 왼쪽 시프트한 후, 그 결과값을 왼쪽의 피연산자에 대입함.
int x = 0B00001111; System.out.printf("%16s","x = "); System.out.println(String.format("%32s",Integer.toBinaryString(x)).replace(" ", "0")); x >>>= 3; System.out.printf("%-12s","x >>>= 3; "); System.out.println("x = " + String.format("%32s",Integer.toBinaryString(x)).replace(" ", "0"));Output(출력)
x = 00000000000000000000000000001111 x >>= 3; x = 00000000000000000000000000000001
int x = -0B00001111; System.out.printf("%16s","x = "); System.out.println(String.format("%32s",Integer.toBinaryString(x)).replace(" ", "0")); x >>>= 3; System.out.printf("%-12s","x >>>= 3; "); System.out.println("x = " + String.format("%32s",Integer.toBinaryString(x)).replace(" ", "0"));Output(출력)
x = 11111111111111111111111111110001 x >>>= 3; x = 00011111111111111111111111111110
🔝 Click here to go to the list of operaters!
(여기를 클릭하여 연산자 리스트로 가세요.)
기타 연산자
Ternary Operator(삼항 연산자)
자바에서 유일하게 피연산자를 세 개나 가지는 조건 연산자
조건식 ? 반환값1(true) : 반환값2(false)물음표(?) 앞의 조건식에 따라
결과값이 참(true) 이면 반환값 1을 반환
결과값이 거짓(false)이면 반환값2를 반환int num1 = 5, num2 = 7; int result; result = (num1 > num2) ? num1 :num2; System.out.println("5와 7 중 더 큰 정수는 " + result + "입니다."); result = (num1 < num2) ? num1 :num2; System.out.println("5와 7 중 더 작은 정수는 " + result + "입니다.");Output(출력)
5와 7 중 더 큰 정수는 7입니다. 5와 7 중 더 작은 정수는 5입니다.
instanceof Operator(instanceof 연산자)
찬조 변수가 참조하고 있는 인스턴스의 실제 타입을 반환해 줍니다.
해당 객체가 어떤 클래스나 인터페이스로부터 생성되었는지를 판별INSTANCE_NAME instanceof CLASS_OR_INTERFACE_NAME왼쪽 피연산자인 인스턴스(INSTANCE_NAME)가 오른쪽 피연산자인 클래스나 인터페이스(CLASS_OR_INTERFACE_NAME)로부터 생성되었으면
true를 반환
그렇지 않으면false를 반환static class A {} static class B extends A {} public static void main(String[] args) { A a = new A(); B b = new B(); System.out.println("a instanceof A : " + Boolean.toString(a instanceof A)); System.out.println("b instanceof A : " + Boolean.toString(b instanceof A)); System.out.println("a instanceof B : " + Boolean.toString(a instanceof B)); // true System.out.println("b instanceof B : " + Boolean.toString(b instanceof B)); // true }Output(출력)
a instanceof A : true b instanceof A : true a instanceof B : false b instanceof B : true
참고 사이트
[java] 비트의 음수 표현과 shift 연산자
[Java] 자바 연산자 (Java Operator)
[Java] 쉬프트 연산자 <<, <<<
[JAVA] 비트 쉬프트(Shift)연산자 : << , >> , >>>
비트 연산자
[JAVA 자바 03] 자바(JAVA) 변수(Variable)와 2진수, 8진수, 16진수




